|
##################################################################
# Las funciones principales son
# 1) dom_fun_gen( lista,f,col)
# dada una lista de
transformaciones, devuelve las imágenes
# por ellas del dominio fundamental
usual de SL_2(Z) y
# colorea hasta altura f con el
color col
# 2) arcc(z1,z2,f,col)
# devuelve el arco de geodésica que
conecta z1 y z2 y se
# colorea hasta altura f con el
color col
##################################################################
def dom_fun_gen( lista,f,col):
P = point( (0,0), size=0 )
for item in lista:
if item[:] ==
[1,0,0,1][:] or item[:] == [-1,0,0,-1][:]:
P += arcc( -1/2+I*sqrt(3)/2,
1/2+I*sqrt(3)/2,f,col )
P +=
line([(-1/2,sqrt(3)/2),(-1/2,f(x=-1/2))], thickness=3,
rgbcolor = col)
P +=
line([(1/2,sqrt(3)/2),(1/2,f(x=1/2))], thickness=3,
rgbcolor = col)
else:
P += triangg( item,f,col)
return P
def triangg( m,f,col):
# Triángulo geodésico
correspondiente a la matriz m
a, b, c, d = m[0], m[1], m[2], m[3]
# Vértices
z2 = (a*(-1+I*sqrt(3))/2 +b)/(
c*(-1+I*sqrt(3))/2+d)
z3 = (a*(1+I*sqrt(3))/2 +b)/(
c*(1+I*sqrt(3))/2+d)
if c == 0:
z1 =
real(z2)+i*f(x=real(z2))
else:
z1 = a/c
P = arcc( z1, z2,f,col)
P += arcc( z2, z3,f,col)
if c == 0:
z1 =
real(z3)+i*f(x=real(z3))
else:
z1 = a/c
P += arcc( z3, z1,f,col)
return P
def arcc(z1,z2,f,col):
# Arco de geodésica que une z1 y z2
c, d = real(z1), imaginary(z1)
a, b = real(z2), imaginary(z2)
# Señala los puntos
P = point( (a,b), size=40, rgbcolor
= col )
P += point( (c,d), size=40,
rgbcolor = col )
# Si es vertical, pinta una línea
if a==c:
P +=
line([(a,b),(c,d)], thickness=3, rgbcolor = col )
return P
# calcula el centro (cent,0)
cent = (a+c)/2+(d-b)*(b+d)/2/(c-a)
R = sqrt((a-cent)^2+b^2)
# Dibuja el arco
P += plot( sqrt(R^2-(x-cent)^2),x,
min(c,a), max(c,a), fill=f, fillcolor= col,
fillalpha=0.5, thickness=3, rgbcolor = col )
return P
#####################
#####################
# CASO COMPACTO G_3
#####################
#####################
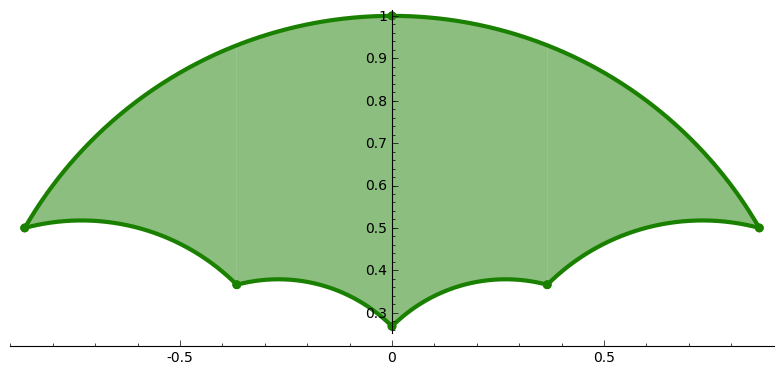
f = sqrt(1-x^2)
col = (0.1,0.5,0)
P = arcc( (-sqrt(3)+I)/2, I, f, col)
P += arcc( I, (sqrt(3)+I)/2, f, col)
P += arcc( (-sqrt(3)+I)/2, (-1+I)/(1+sqrt(3)), f, col)
P += arcc( (-1+I)/(1+sqrt(3)), (2-sqrt(3))*I, f, col)
P += arcc( (2-sqrt(3))*I, (1+I)/(1+sqrt(3)), f, col)
P += arcc( (1+I)/(1+sqrt(3)), (+sqrt(3)+I)/2, f, col)
P.show(aspect_ratio=1)
#####################
#####################
# NO COMPACTO
#####################
#####################
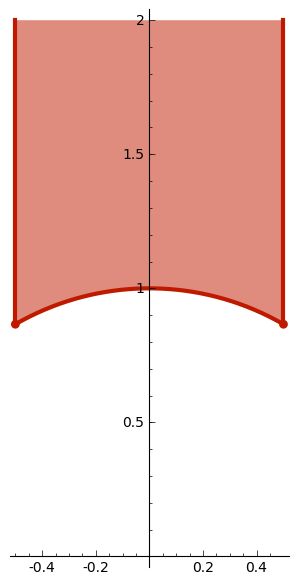
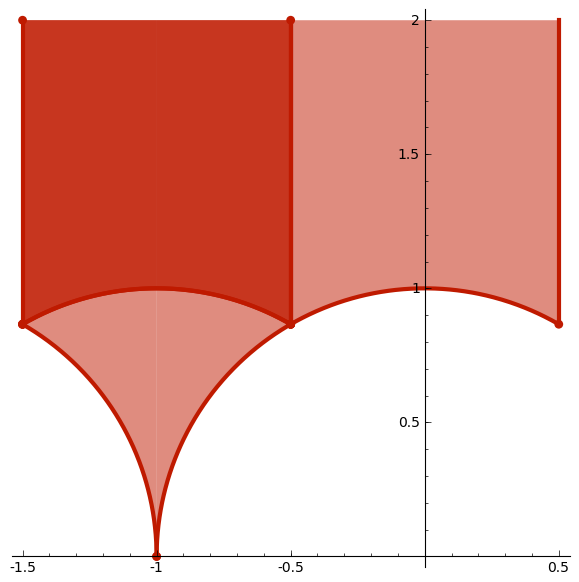
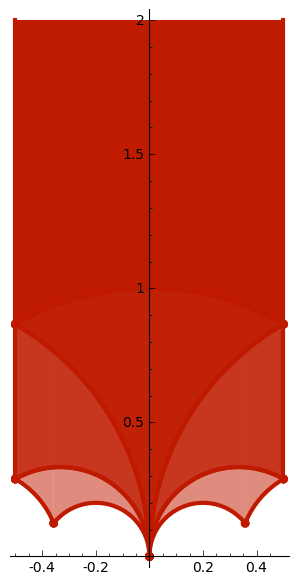
f = 2 + 0*x
col = (0.75,0.1,0)
Gam1 = [[1,0,0,1]] # Modular Gamma_0(1)
dom_fun_gen( Gam1,f,col ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gamtild = Gam1 + [[1,1,-1,0], [1,-1,0,1] ]
#Gammatild
dom_fun_gen( Gamtild,f,col ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam5 = Gam1 + [[0,-1,1,0], [0,-1,1,1], [0,-1,1,-1],
[0,-1,1,2], [0,-1,1,-2] ] #Gamma_0(5)
dom_fun_gen( Gam5,f,col ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
###############################
# LOS GAMMA_0(n) CON n PEQUEÑO
###############################
# La listas de transformaciones las he sacado de
#
https://www.math.lsu.edu/~verrill/fundomain/index2.html
Gam1 = [[1,0,0,1]] # Modular Gamma_0(1)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam1,f,col ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam2 = Gam1 + [[0,-1,1,0], [0,-1,1,1] ] #Gamma_0(2)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam2 ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam3 = Gam2 + [[0,-1,1,-1] ] #Gamma_0(3)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam3 ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam4 = Gam3 + [[0,-1,1,-2], [1,0,2,1] ] #Gamma_0(4)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam4 ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam5 = Gam3 + [[0,-1,1,2], [0,-1,1,-2] ] #Gamma_0(5)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam5 ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam6 = Gam5 + [[0,-1,1,-3], [1,0,2,1], [1,0,3,1],
[-1,0,2,-1], [-1,1,2,-3], [1,1,-3,-2] ] #Gamma_0(6)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam6 ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
Gam7 = Gam5 + [[0,-1,1,3], [0,-1,1,-3]] #Gamma_0(7)
#dom_fun_gen( Gam7 ).show(aspect_ratio=1)
|