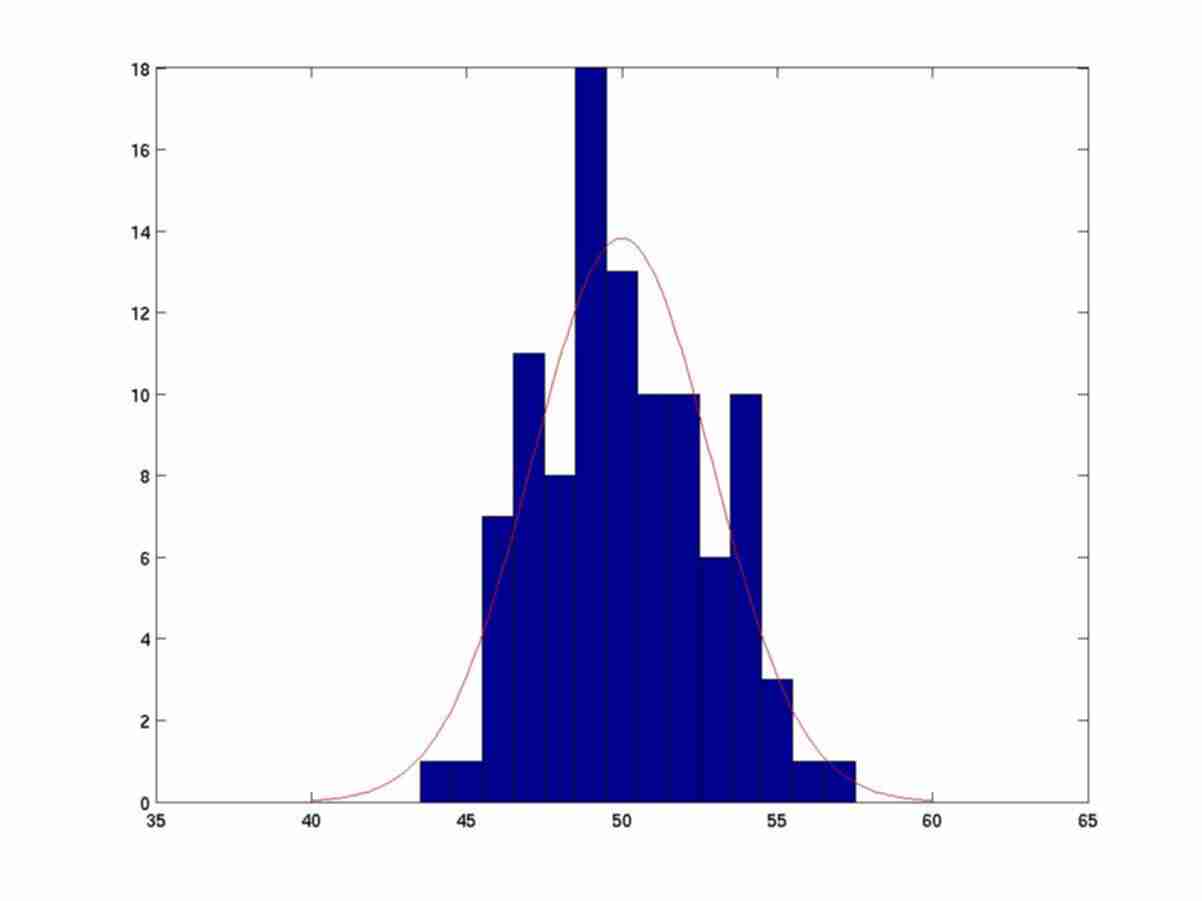
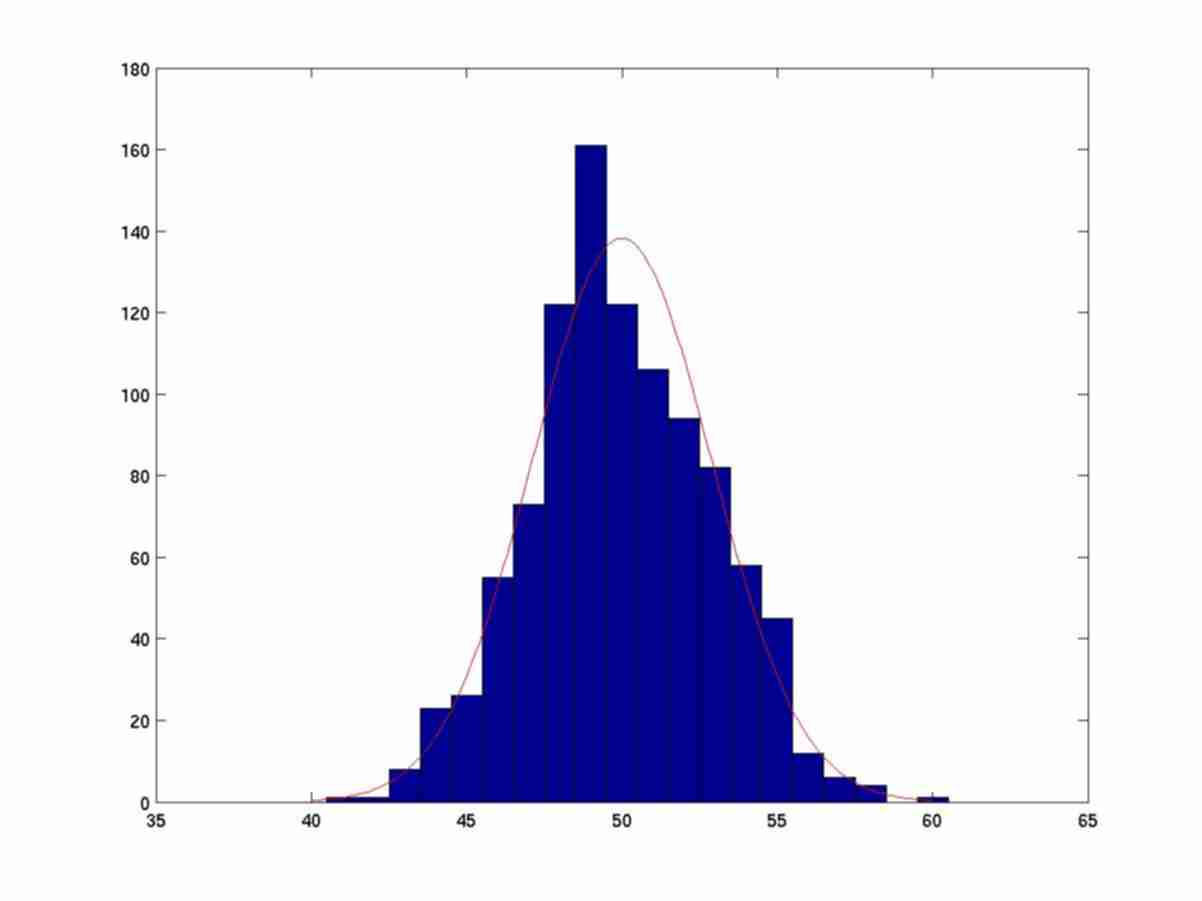
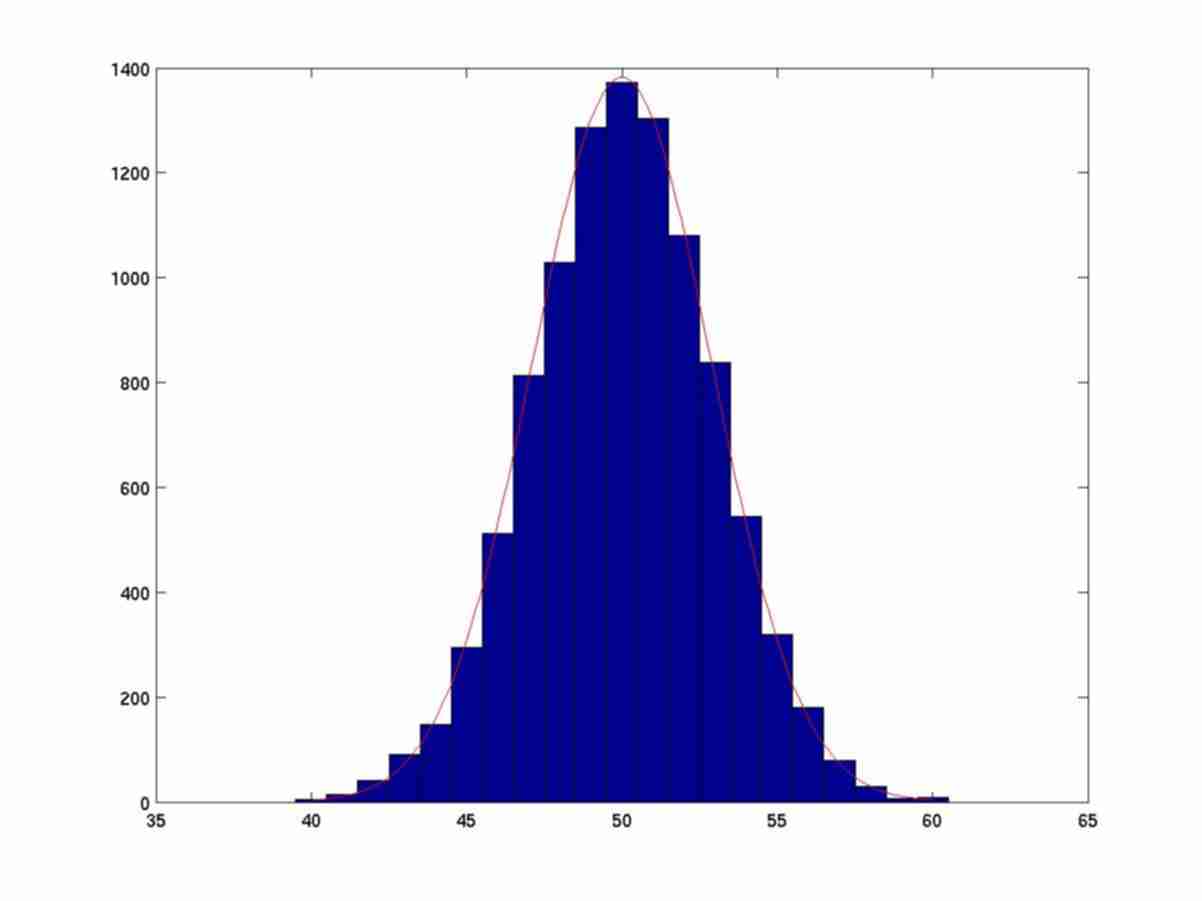
Central limit theorem. In its different versions, roughly speaking, the central limit theorem assures that the sum of independent identically distributed random variables converges to a normal distribution.
The following figures show the histograms of a computer simulation throwing 10 dices and summing the values. The experiment is repeated a number N of times.
 |
 |
 |
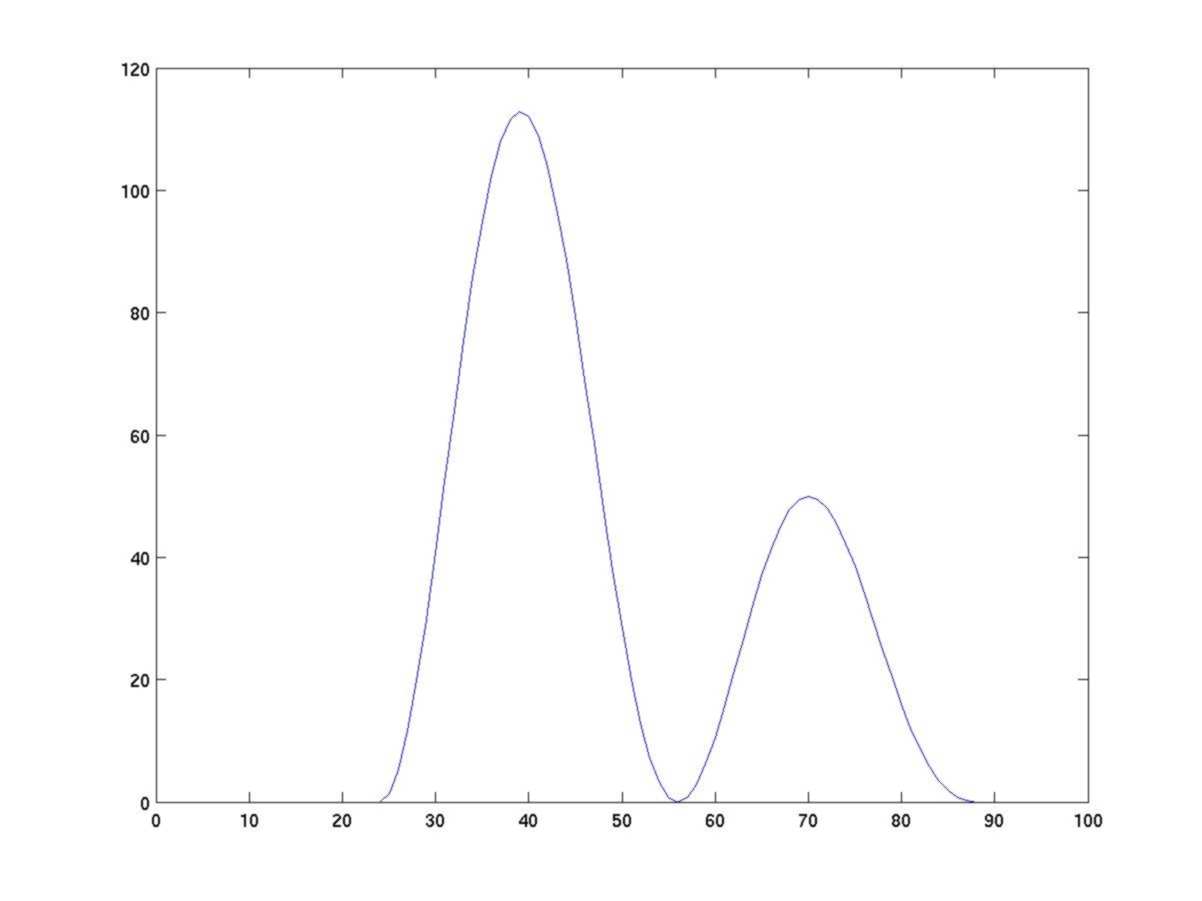
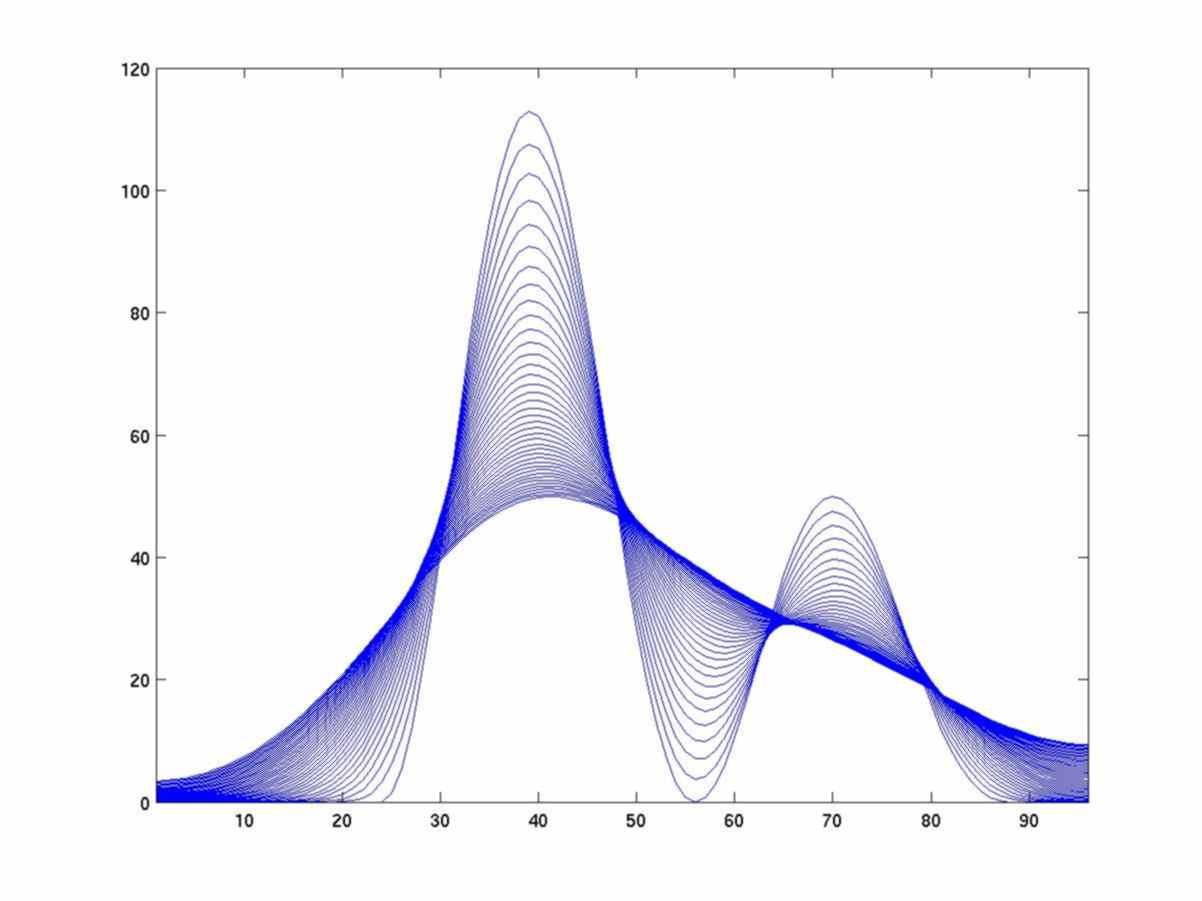
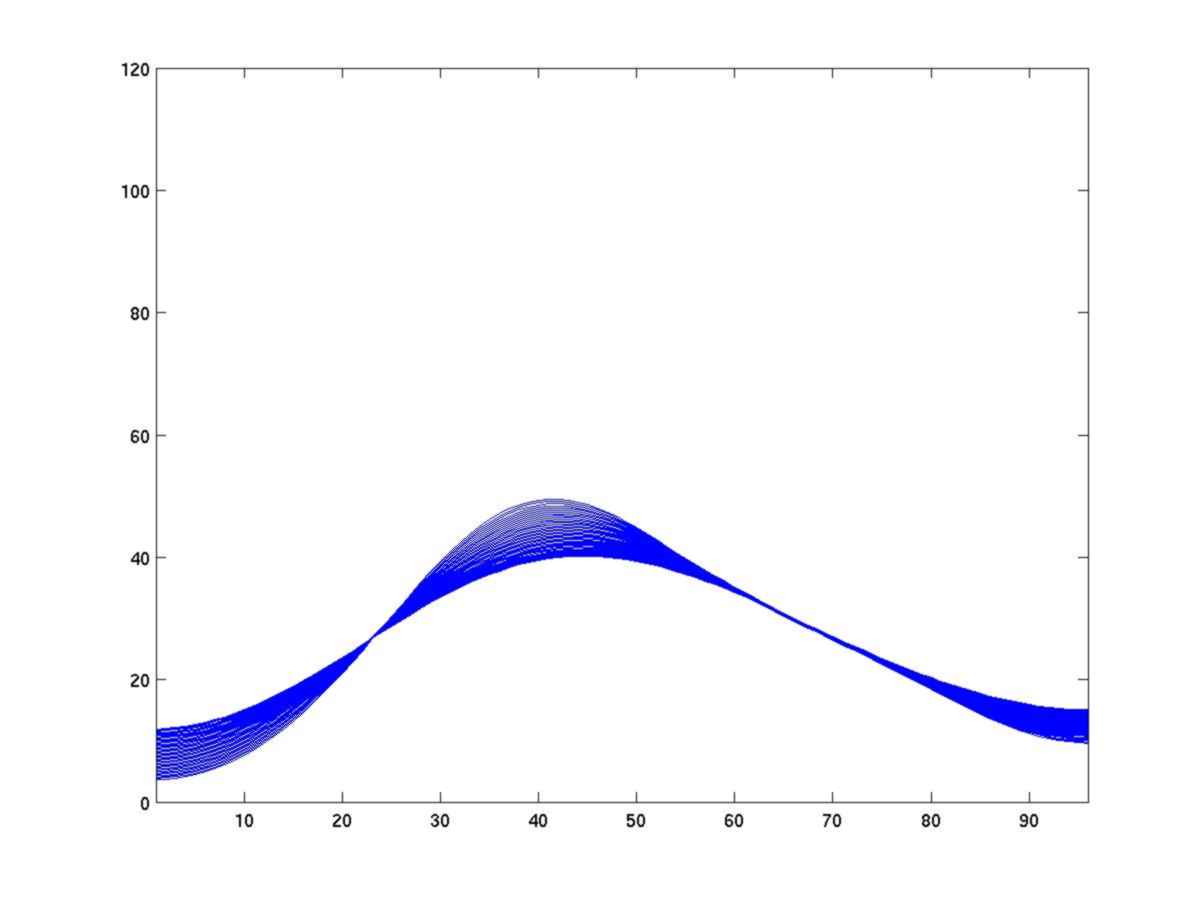
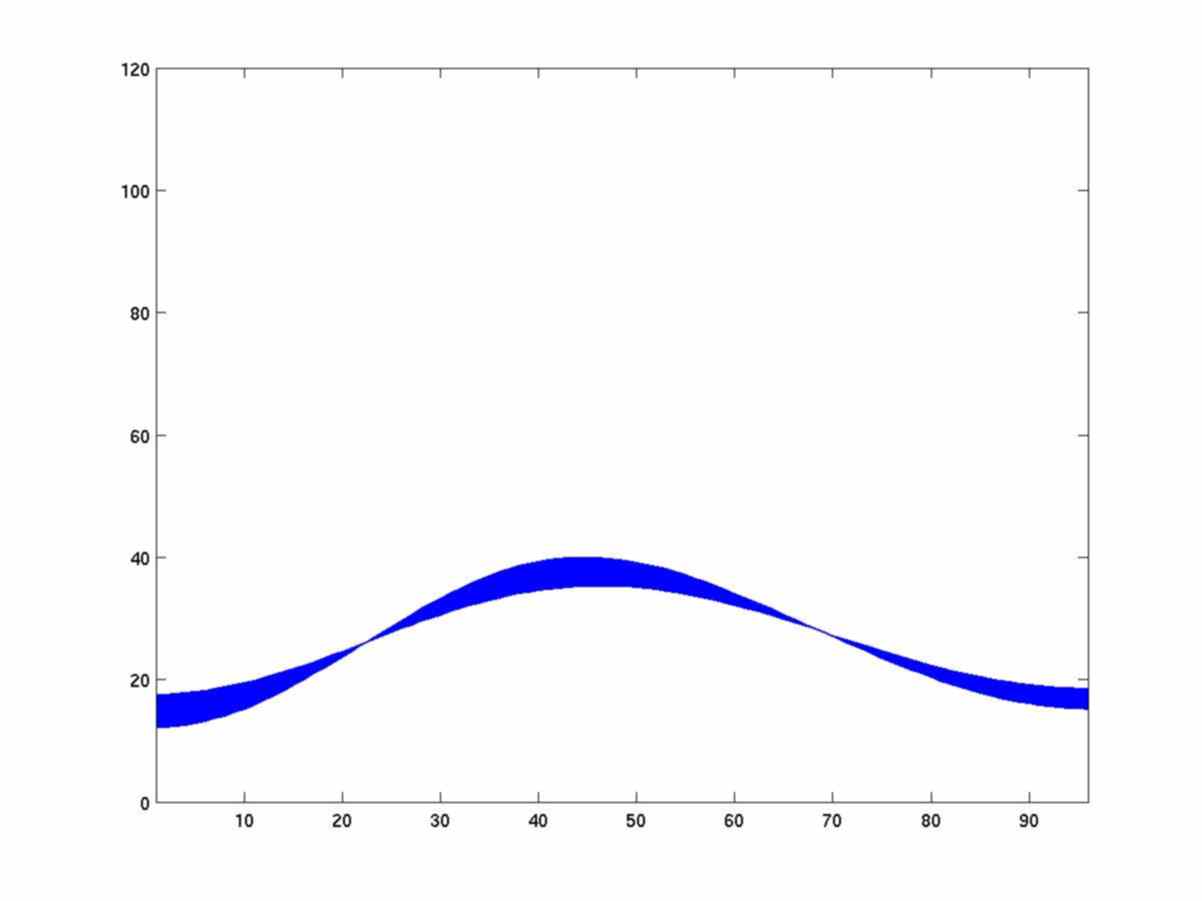
Diffusion. The following figures show the evolution of a simple diffusion process with discrete time and space. The boundary conditions do not allow any loss along the extreme points. The first figure is the initial distribution.
As predicted by the heat equation, the limit distribution tends to be constant.
 |
 |
 |
 |